What is the Simple View of Reading Model?
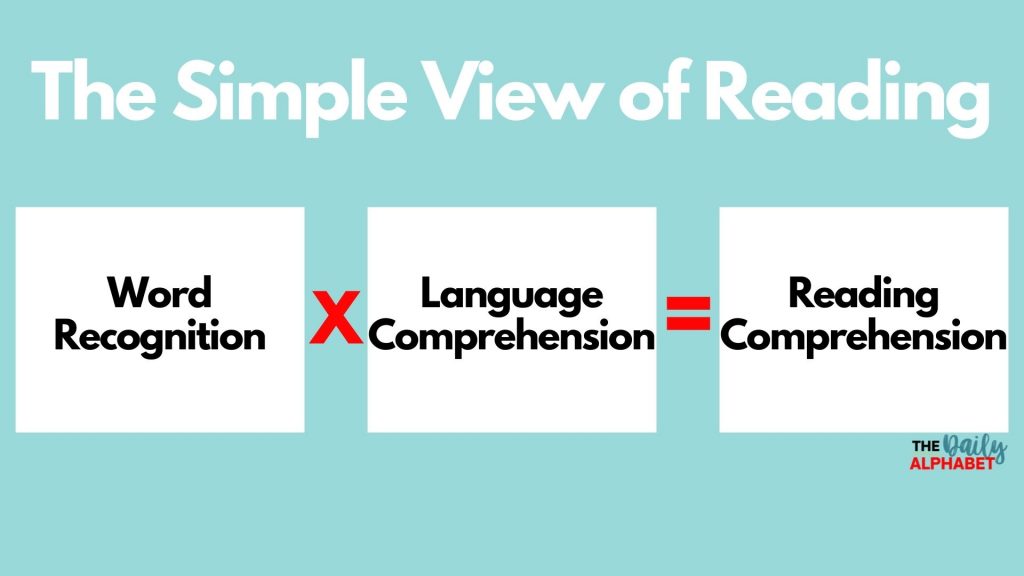
The Simple View of Reading Model posits that reading comprehension is the product of word recognition and language comprehension. It suggests that reading ability is determined by one’s skill in recognizing words accurately and understanding language.
Developed by researchers Gough and Tunmer in 1986, this model has become a fundamental framework in the field of literacy. It underscores the importance of both decoding skills and language comprehension in the process of reading. This model has had a significant impact on educational practices, as it has influenced the development of interventions aimed at improving reading abilities in individuals with reading difficulties.
The Simple View of Reading Model continues to be a foundational concept in the study and teaching of reading comprehension.
1. Introduction To The Simple View Of Reading Model
1. Introduction to the Simple View of Reading Model
1.1 Overview Of The Simple View Of Reading Model
The Simple View of Reading Model is a foundational framework that helps to understand the essential components of reading proficiency. It is a widely accepted model in literacy research and has significant implications for both educators and parents.
1.2 Historical Background
The Simple View of Reading Model was proposed by Gough and Tunmer in 1986. It emerged in response to the ongoing debate about the nature of reading and aimed to provide a clear and concise framework for understanding reading comprehension. Gough and Tunmer argued that reading comprehension can be best understood as a product of two separate but interacting components: decoding skills and language comprehension.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
2. Key Components Of The Simple View Of Reading Model
The Simple View of Reading Model provides a framework for understanding the process of reading, incorporating two key components: decoding and language comprehension.
2.1 Decoding
Decoding refers to the ability to recognize and translate written words into spoken language. It involves skills such as phonemic awareness, understanding letter-sound correspondence, and the ability to blend sounds together to form words.
2.2 Language Comprehension
Language comprehension involves the understanding of vocabulary, grammar, and the ability to derive meaning from text. It encompasses skills such as understanding the main idea, making inferences, and interpreting the deeper meaning of the text.
3. Understanding The Interaction Between Decoding And Language Comprehension
In the Simple View of Reading Model, decoding and language comprehension play vital roles in the reading process. Decoding refers to the ability to accurately translate written words into spoken words, while language comprehension involves understanding the meaning of text. The interaction between these two components is crucial in achieving successful reading comprehension. Let’s explore the importance of decoding and language comprehension, the critical role of phonological decoding, and the significance of syntactic and semantic comprehension.
3.1 Importance Of Decoding And Language Comprehension
In the context of reading, decoding and language comprehension are like two sides of the same coin. Both are necessary for effective reading comprehension. Decoding allows readers to recognize and decode individual words, while language comprehension enables readers to understand the meaning of those words within the context of the text. Without a strong foundation in decoding, it becomes challenging for readers to comprehend the text they are reading.
When decoding skills are well-developed, readers can effortlessly decode words, freeing up cognitive resources for higher-level comprehension processes. On the other hand, strong language comprehension skills enable readers to make connections between words, sentences, and paragraphs, leading to a deeper understanding of the text. These two components work in tandem to facilitate the overall reading process.
3.2 Critical Role Of Phonological Decoding
Phonological decoding plays a critical role in the decoding aspect of reading. It involves the ability to map letters to their corresponding sounds. By recognizing letter-sound relationships, readers are able to decode unfamiliar words and make meaning from the text. The mastery of phonological decoding not only supports fluent reading but also enhances comprehension. When readers can effortlessly decode words, their attention can be focused on understanding the text and making connections between ideas.
Phonological decoding acts as a fundamental building block for reading proficiency. By breaking words down into smaller units (phonemes), readers can decode and blend sounds together to form words. This ability forms the basis of effectively deciphering and pronouncing both familiar and unfamiliar words, thereby enhancing reading comprehension.
3.3 Syntactic And Semantic Comprehension
In addition to decoding, effective language comprehension involves an understanding of both syntactic and semantic aspects of language. Syntactic comprehension refers to the understanding of how words and phrases are structured in a sentence, as well as the rules that govern the arrangement of these elements. Semantic comprehension, on the other hand, focuses on meaning – the understanding of the individual words and the relationships between them.
While decoding is necessary for deciphering individual words, syntactic and semantic comprehension are crucial for making sense of the overall text. The ability to comprehend sentence structure aids readers in understanding the intended meaning and interpreting the relationships between different words and phrases. Semantic comprehension allows readers to assign meaning to words and connect them to prior knowledge, enabling a deeper understanding of the text.
In conclusion, decoding and language comprehension are integral components of the Simple View of Reading Model. Their interaction is essential for achieving successful reading comprehension. Decoding skills, particularly phonological decoding, lay the foundation for accurate word recognition, while syntactic and semantic comprehension help readers derive meaning from the text they are reading. By understanding the relationship between these components, educators and learners can work towards improving reading proficiency and fostering a love for reading.4. Empirical Evidence And Research On The Simple View Of Reading Model
Empirical evidence and research have supported the Simple View of Reading Model, a framework that suggests reading comprehension is the product of decoding and language comprehension abilities. This model emphasizes the importance of both word recognition and comprehension skills in reading development.
The Simple View of Reading (SVR) model has gained significant attention in the field of literacy instruction due to its emphasis on the two crucial components of reading comprehension – decoding and language comprehension. Extensive research and empirical evidence have shed light on the validity and usefulness of this model, making it a cornerstone of reading instruction. In this section, we will explore the various studies supporting the SVR model, analyze criticisms and limitations, as well as discuss the implications of this model for reading instruction.4.1 Studies Supporting The Simple View Of Reading
Several studies have provided empirical support for the Simple View of Reading model, adding to its credibility and applicability in educational settings. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key findings:- Rosenblatt and Pearson (2001) conducted a longitudinal study with a large sample of students across different grade levels and found a strong positive correlation between decoding skills and reading comprehension abilities.
- In a meta-analysis by Gough and Tunmer (2019), multiple studies were reviewed, reaffirming that language comprehension is a essential factor in reading comprehension, as indicated by the SVR model.
- Smith and Wilhelm (2008) conducted a study involving struggling readers and found that improving both decoding and language comprehension skills resulted in significant improvements in reading comprehension.
4.2 Criticisms And Limitations
While the Simple View of Reading model has been widely accepted, it is not without its criticisms and limitations. It is important to acknowledge and critically examine these concerns to gain a comprehensive understanding of the model. Some of the key criticisms include:- The model oversimplifies the complex nature of reading comprehension by reducing it to just two components, potentially neglecting other important factors.
- There is ongoing debate regarding how decoding and language comprehension interact and contribute to reading comprehension. Some argue that the relationship between the two is not as straightforward as proposed by the SVR model.
- The model does not take into account the potential impact of socio-cultural factors on reading comprehension, such as background knowledge and experiences.
4.3 Implications For Reading Instruction
The Simple View of Reading model has significant implications for reading instruction and classroom practices. By recognizing the importance of both decoding and language comprehension, educators can design targeted interventions to support struggling readers and promote overall literacy development. Some potential implications include:- Providing explicit and systematic phonics instruction to improve decoding skills, particularly for early readers.
- Developing strategies to foster language comprehension, such as vocabulary instruction, explicitly teaching reading comprehension strategies, and promoting background knowledge and critical thinking skills.
- Individualized instruction and intervention plans tailored to students’ specific needs and strengths in both decoding and language comprehension.
5. Practical Applications Of The Simple View Of Reading Model
The Simple View of Reading Model is an essential framework that helps educators understand the complex process of reading and address reading difficulties effectively. By recognizing the two core components of reading, decoding and language comprehension, this model provides practical strategies to support struggling readers and promote reading comprehension skills. Here are some key applications of the Simple View of Reading Model:
5.1 Assessing Reading Difficulties
Assessing reading difficulties is crucial to identify the specific areas where struggling readers need support. By applying the Simple View of Reading Model, teachers can conduct comprehensive assessments that target both decoding and language comprehension abilities. This assessment process enables educators to pinpoint areas of weakness and tailor interventions accordingly.
There are various assessment methods that can be used, such as:
Representing info as Table
| Assessment Method | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Phonological Awareness Assessment | Identify difficulties in recognizing and manipulating sounds in words. |
| Reading Fluency Assessment | Evaluate the speed, accuracy, and expression in reading. |
| Reading Comprehension Assessment | Measure understanding of text at different levels. |
5.2 Designing Effective Interventions
Once reading difficulties have been identified, designing effective interventions becomes crucial for improving reading skills. Using the Simple View of Reading Model, teachers can create targeted interventions that focus on enhancing both decoding and language comprehension abilities. These interventions may include:
- Phonics instruction to improve decoding skills
- Vocabulary development activities to enhance language comprehension
- Reading fluency exercises to strengthen reading speed and accuracy
- Comprehension strategies, such as summarizing and making connections, to improve overall understanding
5.3 Promoting Reading Comprehension Skills
Reading comprehension is a critical aspect of successful reading. The Simple View of Reading Model emphasizes the importance of language comprehension in developing strong reading comprehension skills. To promote reading comprehension, educators can implement the following strategies:
- Explicitly teach comprehension strategies, such as predicting, questioning, and summarizing.
- Encourage active engagement with the text through discussions and annotations.
- Provide opportunities for students to read a variety of genres to broaden their understanding.
- Foster metacognitive awareness by teaching students to monitor their understanding and make adjustments as needed.
By applying the principles of the Simple View of Reading Model, educators can unlock the potential of struggling readers and empower them to become confident and skilled readers. Through a targeted assessment process, effective interventions, and a focus on reading comprehension, teachers can provide the necessary support for every student’s reading journey.
Credit: www.researchgate.net

Credit: ortongillinghamonlinetutor.com
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is The Simple View Of Reading Model?
What Is The Simple View Of Reading Approach?
The Simple View of Reading approach analyzes reading as a combination of decoding and language comprehension. It suggests that reading ability is determined by the interaction of these two components. This model is a foundational theory used to understand reading development and provides insights into literacy instruction.
What Is The Simple View Of Reading Source?
The Simple View of Reading source explains the two key components of reading: decoding and comprehension. It helps understand how these components interact to determine reading ability.
Why Was The Simple View Of Reading Introduced?
The Simple View of Reading was introduced to provide a clear framework for understanding reading comprehension. It combines reading decoding and language comprehension to explain the process of reading. This view helps identify and address difficulties in reading, leading to improved literacy outcomes.
Conclusion
The Simple View of Reading Model provides a comprehensive understanding of the reading process. By combining decoding and language comprehension, it emphasizes the crucial factors that contribute to a person’s reading ability. This model has proven to be effective in guiding educators and researchers in their efforts to improve reading instruction and intervention programs.
By implementing the Simple View of Reading Model, educators can better support students in developing strong reading skills and achieving academic success.