How Do You Measure Oral Reading Fluency?
Oral reading fluency is measured by timing a student as they read a passage and calculating the number of words read correctly per minute. This measure provides an indication of a student’s reading speed, accuracy, and prosody.
Oral reading fluency is an essential component of reading assessment, as it assesses a student’s ability to read aloud smoothly and with expression. The process involves timing a student as they read a grade-level text and then calculating their reading rate, accuracy, and expression.
This measure can indicate the student’s overall reading proficiency and identify areas that may need improvement. By using this assessment, educators can track a student’s progress in reading fluency over time and tailor their instruction to support individual student needs. Effective assessment and monitoring of oral reading fluency are critical for promoting reading comprehension and overall literacy skills.
Why Measure Oral Reading Fluency?
When it comes to assessing a student’s reading skills, measuring oral reading fluency is a crucial aspect. Oral reading fluency refers to the ability to read with accuracy, speed, and proper expression. By evaluating a student’s oral reading fluency, educators gain valuable insights into their reading comprehension, decoding skills, and overall proficiency. This helps in identifying areas of improvement and designing targeted interventions.
Importance Of Oral Reading Fluency:
Oral reading fluency plays a significant role in a child’s reading development and academic success. Here’s why measuring oral reading fluency is so important:
- Assessment: Oral reading fluency assessments provide educators with reliable and objective data about a student’s reading performance.
- Early Identification: Measuring oral reading fluency helps in identifying struggling readers at an early stage, enabling timely intervention and support.
- Tracking Progress: Regular assessments of oral reading fluency allow educators to track a student’s progress over time, making it easier to gauge the effectiveness of interventions or instructional strategies.
Benefits Of Measuring Oral Reading Fluency:
There are numerous benefits to measuring oral reading fluency. Here are just a few:
- Diagnostic Insights: Assessing oral reading fluency helps in diagnostic decision-making by highlighting specific areas of weakness, such as word recognition or prosody.
- Individualized Instruction: By knowing a student’s oral reading fluency, educators can tailor instruction to meet their individual needs, ensuring they receive targeted support.
- Motivation and Engagement: Regular measurement of oral reading fluency motivates students to improve their reading skills and fosters engagement with text.
- Evidence-Based Interventions: Oral reading fluency assessments guide educators in choosing evidence-based interventions that directly address the identified reading weaknesses. This increases the effectiveness of interventions.

Credit: www.talesfromoutsidetheclassroom.com
Key Elements Of Oral Reading Fluency
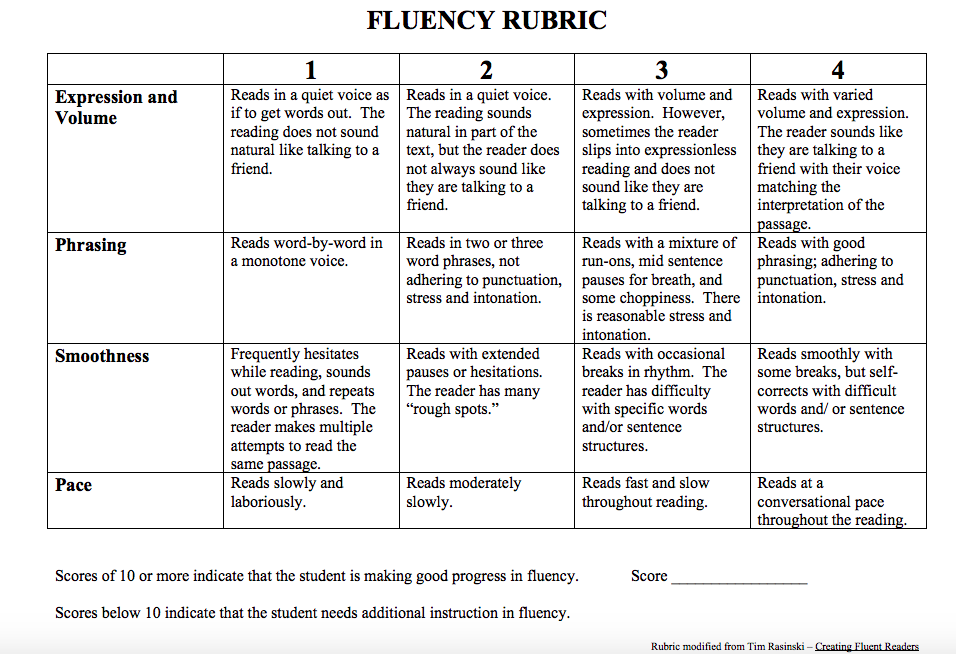
When it comes to assessing oral reading fluency, it’s essential to understand the key elements that contribute to a student’s proficiency in this area. By focusing on the foundational aspects of oral reading fluency, educators can effectively measure and support their students’ progress. This blog post will explore the key elements of oral reading fluency with a specific focus on accuracy, rate, and fluency.
Accuracy
Accuracy in oral reading fluency refers to the student’s ability to read words correctly. It’s measured by analyzing the number of errors a student makes while reading a designated passage. By identifying and tallying these errors, educators can gauge a student’s accuracy level and determine whether additional support and intervention are needed.
Rate
The rate of oral reading fluency assesses how quickly a student can read a passage while maintaining accuracy. It’s calculated by examining the number of words a student can read within a specified time frame. By measuring reading rate, educators can determine the efficiency and speed at which a student processes written text, identifying areas for improvement and monitoring progress over time.
Fluency
Fluency encompasses the smoothness, expression, and natural flow of a student’s oral reading. It reflects how well a student comprehends and interprets the text while reading aloud. By observing the fluidity and tone of a student’s oral reading, educators can evaluate their overall fluency and pinpoint areas where additional support and practice may be beneficial.
Types Of Assessments For Measuring Oral Reading Fluency
When assessing oral reading fluency, educators use various types of measurements to gauge a student’s progress and proficiency. These assessments provide valuable insights into a student’s reading abilities and help educators tailor their instruction to meet individual needs.
Running Records
One of the most widely used assessments for measuring oral reading fluency is the running record. Educators closely observe a student’s reading, recording errors, self-corrections, and fluency. These records offer valuable data on reading rate, accuracy, and prosody, providing a comprehensive view of a student’s oral reading skills.
Oral Reading Fluency Passages
Using oral reading fluency passages is another common method to assess a student’s reading fluency. These passages are carefully selected to suit the student’s reading level, offering an opportunity for the student to read aloud while the educator evaluates their fluency, expression, and comprehension. These assessments help identify areas for improvement and track progress over time.
Curriculum-based Measurement
Curriculum-based measurement (CBM) is an effective tool for measuring oral reading fluency. Educators use CBM to regularly assess a student’s reading performance using brief, standardized passages. This method allows for frequent monitoring of progress and helps identify any instructional adjustments needed to support the student’s reading development.
Guidelines For Administering Oral Reading Fluency Assessments
When it comes to assessing students’ oral reading fluency, it is essential to follow specific guidelines to ensure accurate and reliable results. These guidelines involve selecting appropriate texts, setting a time limit, and establishing scoring criteria. By adhering to these guidelines, educators can effectively measure students’ reading fluency and identify areas for improvement. Let’s explore each of these guidelines in detail.
Selecting Appropriate Texts
Selecting the right text for an oral reading fluency assessment is crucial to ensure that students are reading at an appropriate difficulty level. If the text is too easy, it may not accurately reflect a student’s true reading abilities. On the other hand, if the text is too challenging, it can lead to frustration and disengagement. To choose appropriate texts, consider the average reading level of the students being assessed. Using text leveling systems, such as Lexile or Fountas and Pinnell, can help determine the right difficulty level for each student.
Setting A Time Limit
To measure oral reading fluency effectively, it is important to adhere to a specific time limit for each assessment. This time limit ensures consistency across different students and allows for meaningful comparisons. Typically, oral reading fluency assessments are timed for one minute. During this time, the student reads aloud as much of the text as possible. Setting a time limit also helps provide a standard measurement of reading speed and accuracy, enabling educators to track progress over time.
Establishing Scoring Criteria
When administering oral reading fluency assessments, having clear scoring criteria is essential to ensure consistency and objectivity in assessment results. Scoring criteria typically include two main components: reading rate (words read per minute) and accuracy. For reading rate, educators count the number of words read correctly within the designated time frame. Accuracy is determined by evaluating correct word pronunciation and recognition. By establishing precise scoring criteria, educators can effectively evaluate students’ overall reading fluency and identify areas that need further support.
Interpreting And Using Oral Reading Fluency Data
Interpreting and using oral reading fluency data is crucial for assessing and improving students’ reading skills. By analyzing the data obtained from oral reading fluency assessments, teachers can identify reading difficulties, monitor progress, and inform instructional planning. Let’s delve into each of these aspects and understand how oral reading fluency data can be effectively utilized in the learning process.
Identifying Reading Difficulties
Oral reading fluency assessments provide valuable insights into a student’s reading abilities and any potential reading difficulties they may be experiencing. By measuring factors such as accuracy, speed, and expression, teachers can identify areas where students may be struggling. This data allows teachers to pinpoint specific skills that need improvement, such as decoding, sight word recognition, or comprehension.
Monitoring Progress
Regularly measuring oral reading fluency and tracking the results over time enables teachers to monitor students’ progress in their reading skills. By comparing fluency rates from one assessment to the next, teachers can observe if students are making significant improvements or if additional support and interventions are required. This data-driven approach ensures that students receive the necessary guidance and helps identify potential difficulties early on.
Informing Instructional Planning
Oral reading fluency data serves as a valuable tool for teachers when planning their instruction. The insights gained from these assessments allow teachers to tailor their teaching methods, materials, and strategies to meet each student’s specific needs. This personalized approach ensures that students are receiving instruction that is both challenging and supportive, promoting further growth in their reading skills.
Overall, interpreting and using oral reading fluency data is essential for effective reading instruction. By identifying reading difficulties, monitoring progress, and informing instructional planning, teachers can address individual students’ needs and facilitate their development as confident and proficient readers.
Credit: teach.mapnwea.org

Credit: m.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions On How Do You Measure Oral Reading Fluency?
How Do You Track Oral Reading Fluency?
To track oral reading fluency, use tools such as timed reading assessments, audio recordings, and comprehension checks. By measuring reading rate, accuracy, and prosody, educators can evaluate a student’s fluency level. Regular assessments help monitor progress and determine areas where improvement is needed.
How Do You Score Oral Fluency?
Oral fluency is scored by evaluating the speaker’s ability to express themselves effectively and smoothly. Factors such as pronunciation, grammar, vocabulary, and coherence are taken into consideration. The score reflects the speaker’s proficiency in communicating ideas and thoughts clearly and confidently.
How Do You Test Oral Fluency?
Oral fluency is tested by assessing a person’s ability to speak fluently and coherently. This usually involves activities such as reading aloud, giving a presentation, and engaging in conversations. Evaluators analyze the individual’s pace, pronunciation, and overall fluidity in speaking.
Conclusion
Measuring oral reading fluency is crucial for assessing a student’s reading skills. By utilizing tools like timed reading passages, tracking words per minute, and evaluating accuracy, educators can determine a student’s reading rate and comprehension. This information helps tailor instructional strategies to improve fluency skills.
Incorporating these measurements regularly ensures students’ progress in their reading abilities, fostering a lifelong love for learning.